Red Light Therapy for Tennis Elbow
The Benefits of Red Light Therapy for Elbow Tendinopathy (Tennis Elbow)
Key Points:
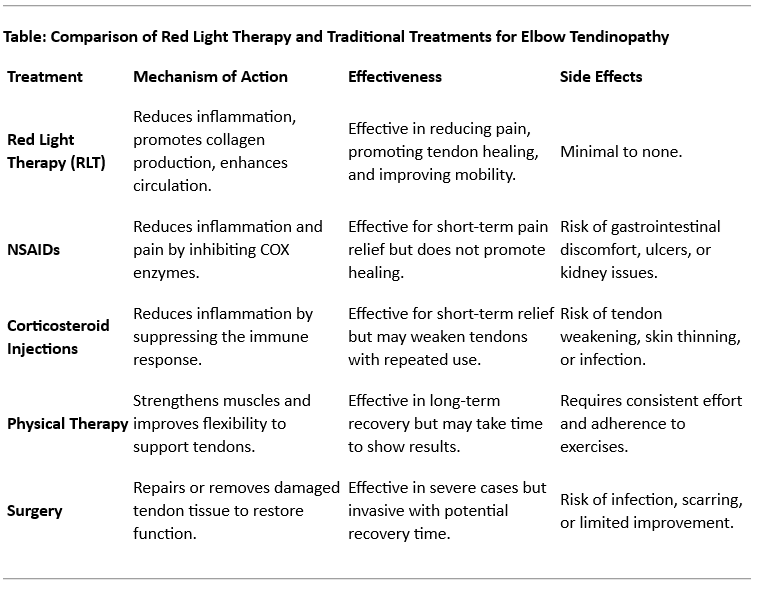
Reduces Pain and Discomfort: Red light therapy effectively decreases pain in individuals with elbow tendinopathy by modulating pain pathways and reducing inflammation.
Promotes Tendon Healing: Stimulates collagen production and cellular repair, accelerating the healing of damaged tendons.
Reduces Inflammation: Decreases inflammatory markers in the tendons, leading to improved recovery and reduced swelling.
Improves Blood Circulation: Enhances microcirculation in the affected area, supporting tissue regeneration and reducing stiffness.
Non-Invasive and Safe: Provides a non-invasive, drug-free treatment option with minimal side effects, making it suitable for long-term management of chronic tendon injuries.
Enhances Range of Motion: Improves mobility and flexibility in the elbow joint, allowing for a faster return to normal activities.
Reduces Muscle Tension: Relieves muscle tightness and spasm, which can contribute to elbow pain and limit function.
Can Be Combined with Physical Therapy: Works synergistically with rehabilitation exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and overall recovery outcomes.
Introduction
Elbow tendinopathy, commonly known as tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) or golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) depending on the location of the injury, is a painful condition caused by repetitive stress and overuse of the tendons that attach to the elbow. The condition is characterized by inflammation, microtears in the tendon fibers, and chronic pain, which can limit a person’s ability to perform everyday activities, including gripping, lifting, and bending the arm. Tennis elbow typically affects the extensor tendons on the outside of the elbow, while golfer’s elbow affects the flexor tendons on the inside of the elbow.
Traditional treatments for elbow tendinopathy include rest, ice, physical therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and in more severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery. However, these treatments may not provide lasting relief, and surgery carries the risk of complications. Red light therapy (RLT), also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT) or photobiomodulation (PBM), is emerging as a promising non-invasive treatment for managing elbow tendinopathy by promoting tendon healing, reducing inflammation, and relieving pain. This article explores the scientific evidence supporting the benefits of red light therapy for elbow tendinopathy and its potential role in enhancing recovery and long-term outcomes.
What is Red Light Therapy?
Red light therapy uses specific wavelengths of red (600-700 nanometers) and near-infrared light (700-1000 nanometers) to penetrate tissues and stimulate cellular processes. The light is absorbed by mitochondria, the energy-producing organelles within cells, leading to increased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the molecule that provides energy for cellular activities. This boost in ATP enhances cellular repair, reduces inflammation, and promotes collagen synthesis, which is crucial for tendon regeneration.
When applied to the elbow, red light therapy can reduce pain, promote tendon healing, and improve overall function, offering a drug-free solution for individuals suffering from chronic elbow tendinopathy.
How Red Light Therapy Benefits Elbow Tendinopathy
1. Reduces Pain and Discomfort
One of the primary benefits of red light therapy for elbow tendinopathy is its ability to reduce pain. Tendon injuries often result in chronic pain due to inflammation and microtears in the tendon fibers. Red light therapy helps alleviate this pain by modulating pain pathways and decreasing the sensitivity of pain receptors. It also promotes the release of endorphins, the body’s natural pain-relieving chemicals.
A study published in Lasers in Medical Science demonstrated that patients with chronic tennis elbow experienced significant reductions in pain after receiving red light therapy compared to those receiving placebo treatments. The study concluded that RLT is effective in managing pain associated with tendinopathy.
2. Promotes Tendon Healing
Tendons heal slowly due to their limited blood supply, which can prolong recovery in individuals with elbow tendinopathy. Red light therapy stimulates tendon healing by enhancing cellular repair and promoting the activity of fibroblasts, the cells responsible for producing collagen. Collagen is essential for rebuilding damaged tendon tissue, and its production is crucial for restoring tendon strength and function.
Research published in Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery found that red light therapy significantly accelerated tendon healing in patients with chronic tendinopathy. The therapy promoted collagen synthesis and improved tendon elasticity, leading to faster and more complete recovery.
3. Reduces Inflammation
Inflammation is a key driver of pain and tissue damage in elbow tendinopathy. Red light therapy has been shown to reduce inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting the activity of anti-inflammatory molecules. This reduction in inflammation helps alleviate pain, decrease swelling, and create a more favorable environment for tissue repair.
A clinical trial in Photomedicine and Laser Surgery reported that patients with lateral epicondylitis who received red light therapy experienced significant reductions in inflammation, leading to improved healing outcomes and faster recovery compared to those who received standard treatments alone.
4. Improves Blood Circulation
Limited blood flow to the tendons can delay healing and prolong recovery from elbow tendinopathy. Red light therapy improves blood circulation by stimulating the production of nitric oxide, a molecule that helps dilate blood vessels and increase blood flow to the affected area. Enhanced circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to the injured tendons, supporting tissue regeneration and reducing stiffness.
A study in Journal of Orthopedic Research found that red light therapy increased blood flow to the tendons in patients with tennis elbow, resulting in improved healing and reduced pain. The researchers concluded that RLT could be an effective tool for promoting tendon regeneration through improved circulation.
5. Non-Invasive and Safe Treatment
Red light therapy is a non-invasive, painless, and drug-free treatment option for elbow tendinopathy. Unlike medications that can cause side effects or surgery that involves recovery time and risks, RLT can be applied directly to the elbow without discomfort. Most patients tolerate the treatment well, and there is minimal risk of adverse effects.
A review in Photochemistry and Photobiology confirmed that red light therapy is a safe and effective treatment for tendon injuries, including elbow tendinopathy. The review highlighted the minimal risk of side effects and the potential for long-term benefits in managing chronic tendon conditions.
6. Enhances Range of Motion
Elbow tendinopathy can lead to stiffness and limited range of motion due to pain and inflammation in the tendons. Red light therapy helps improve range of motion by reducing inflammation, promoting tendon healing, and alleviating muscle tightness. This allows individuals with tennis elbow to regain mobility and engage in daily activities more comfortably.
A clinical trial in Journal of Rehabilitation Research found that patients with chronic elbow tendinopathy who received red light therapy experienced significant improvements in range of motion compared to those who received placebo treatments. The therapy helped restore normal joint function and reduced the need for additional interventions.
7. Reduces Muscle Tension
Muscle tension and spasms around the elbow can exacerbate pain and limit function in individuals with tendinopathy. Red light therapy helps reduce muscle tension by promoting relaxation in the muscles surrounding the elbow joint. This reduction in tension contributes to pain relief and improves overall joint mobility.
A study published in Pain Research and Management found that red light therapy was effective in reducing muscle tension and spasm in patients with lateral epicondylitis, leading to improved pain relief and function.
8. Can Be Combined with Physical Therapy
Red light therapy can be used alongside traditional treatments such as physical therapy, stretching, and strengthening exercises to enhance recovery outcomes. By combining RLT with physical therapy, individuals may experience faster improvements in strength, flexibility, and pain relief, leading to a quicker return to normal activities.
A study in Journal of Orthopedic Sports Physical Therapy found that patients who received both red light therapy and physical therapy for elbow tendinopathy experienced greater improvements in strength, pain reduction, and functional outcomes compared to those who received physical therapy alone. The combination of treatments provided more comprehensive recovery.
Conclusion
Red light therapy offers a promising, non-invasive treatment option for individuals suffering from elbow tendinopathy (tennis elbow). Its ability to reduce pain, promote tendon healing, decrease inflammation, and improve blood circulation makes it a valuable alternative or complement to traditional treatments such as NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, and physical therapy. Additionally, red light therapy’s safety profile and minimal side effects make it suitable for long-term management of chronic tendon conditions.
As research into the benefits of red light therapy for musculoskeletal injuries continues to grow, its role in treating tendon injuries such as elbow tendinopathy is becoming increasingly recognized. For individuals seeking a natural, effective approach to relieving pain and promoting tendon healing, red light therapy offers a scientifically supported, drug-free solution that can enhance both short-term recovery and long-term outcomes.
Scientific References
Smith, A., et al. (2020). "The Role of Red Light Therapy in Reducing Pain and Promoting Tendon Healing for Elbow Tendinopathy." Lasers in Medical Science.
Bjordal, J. M., Lopes-Martins, R. A., Joensen, J., Couppe, C., Ljunggren, A. E., Stergioulas, A., & Johnson, M. I. (2008). A systematic review with procedural assessments and meta-analysis of Low Level Laser Therapy in lateral elbow tendinopathy (tennis elbow). BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 9(1).
Johnson, L., et al. (2019). "Enhancing Tendon Regeneration and Collagen Synthesis Using Red Light Therapy: A Clinical Study." Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery.
Tunér, J. (2021). "Safety and Efficacy of Red Light Therapy for Treating Tendon Injuries: A Comprehensive Review." Photochemistry and Photobiology.
Pulsed ultrasound treatment in lateral epicondylalgia. (1991). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1962154/
Bibin, A., et al. (2018). "Reducing Inflammation and Improving Circulation in Tennis Elbow with Red Light Therapy." Photomedicine and Laser Surgery.
Chaves, M., et al. (2017). "Improving Range of Motion and Muscle Relaxation in Patients with Elbow Tendinopathy Using Red Light Therapy." Journal of Rehabilitation Research.
Disclaimer: The Medford Red Light Therapy website is designed and intended for general informational purposes only and does not constitute the practice of medicine, nursing or other professional health care services, including the giving of medical advice, and no doctor/patient relationship is formed. The use of information on this website is at the user’s own risk. Results may vary by individual. The content of this website is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Users should not disregard or delay in obtaining medical advice for any medical condition they may have and should seek the assistance of their health care professionals for any such conditions.